| Cat.#: S220592 |
| Product Name: Anti-HAS1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody |
| Synonyms: HAS |
| UNIPROT ID: Q92839 (Gene Accession – NP_001514 ) |
| Background: Hyaluronan or hyaluronic acid (HA) is a high molecular weight unbranched polysaccharide synthesized by a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to mammals, and is a constituent of the extracellular matrix. It consists of alternating glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine residues that are linked by beta-1-3 and beta-1-4 glycosidic bonds. HA is synthesized by membrane-bound synthase at the inner surface of the plasma membrane, and the chains are extruded through pore-like structures into the extracellular space. It serves a variety of functions, including space filling, lubrication of joints, and provision of a matrix through which cells can migrate. HA is actively produced during wound healing and tissue repair to provide a framework for ingrowth of blood vessels and fibroblasts. Changes in the serum concentration of HA are associated with inflammatory and degenerative arthropathies such as rheumatoid arthritis. In addition, the interaction of HA with the leukocyte receptor CD44 is important in tissue-specific homing by leukocytes, and overexpression of HA receptors has been correlated with tumor metastasis. HAS1 is a member of the newly identified vertebrate gene family encoding putative hyaluronan synthases, and its amino acid sequence shows significant homology to the hasA gene product of Streptococcus pyogenes, a glycosaminoglycan synthetase (DG42) from Xenopus laevis, and a recently described murine hyaluronan synthase. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| Immunogen: Synthetic peptide of human HAS1 |
| Applications: ELISA, IHC |
| Recommended Dilutions: IHC: 50-200; ELISA: 5000-10000 |
| Host Species: Rabbit |
| Clonality: Rabbit Polyclonal |
| Isotype: Immunogen-specific rabbit IgG |
| Purification: Antigen affinity purification |
| Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse |
| Constituents: PBS (without Mg2+ and Ca2+), pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% Sodium Azide and 40% glycerol |
| Research Areas: Signal Transduction, Neuroscience, Cardiovascular, Developmental Biology |
| Storage & Shipping: Store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing |
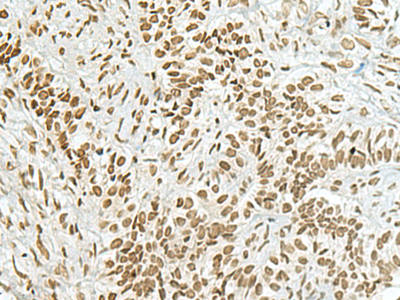
Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin embedded Human ovarian cancer tissue using 220592(HAS1 Antibody) at a dilution of 1/70(Nucleus). | 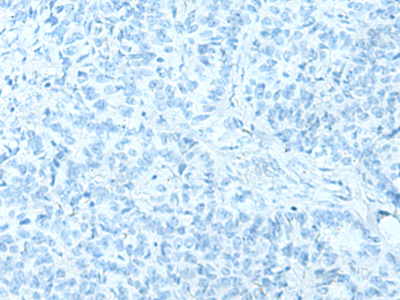
In comparision with the IHC on the left, the same paraffin-embedded Human ovarian cancer tissue is first treated with the synthetic peptide and then with 220592(Anti-HAS1 Antibody) at dilution 1/70. | 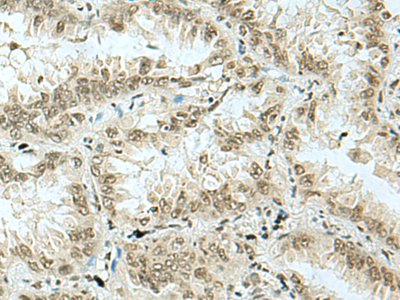
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human lung cancer tissue using 220592(Anti-HAS1 Antibody) at a dilution of 1/70. | 
In comparision with the IHC on the left, the same paraffin-embedded Human lung cancer tissue is first treated with synthetic peptide and then with D261735(Anti-HAS1 Antibody) at dilution 1/70. |
|