Published Pictures for 26907 Gαo-GTP mAb
2.4. Immunoprecipitation of Activated Gα o Subunit
The Gα o activation assay kit from New East Bioscience (#80901, King of Prussia, PA) was used. The protocol recommended by the manufacturer was employed with modifications. Briefly, neurons at 14 days in vitro (DIV) (seeded at 900,000 cells/well) were treated with 1 μM Mas-7 for 5 or 30 min. Then, the cells were lysed with 0.5 mL 1x kit buffer (#30303) and centrifuged at 12,000 ×g 4°C for 10 min. The supernatants were incubated with 1 μL mouse monoclonal antibody specific for Gα o bound to GTP (active form) (#26907) and 20 μL A/G agarose beads (#30301) for 2 h at 4°C with orbital rotation. As a positive control, untreated neurons were lysed and then incubated with 10 mM GTPγS (#30302) and 10 mM MgCl2 for 90 min at RT, and as a negative control, the lysed neurons were incubated with 10 mM GDP (#30304) and 10 mM MgCl2. Later, the lysates were washed 3 times and the beads were suspended in 20 μL Laemmli 2x loading buffer and boiled for 5 min. The total level of Gα o was detected by immunoblotting with a polyclonal anti-Gα o antibody (#21015, 1 : 1000).
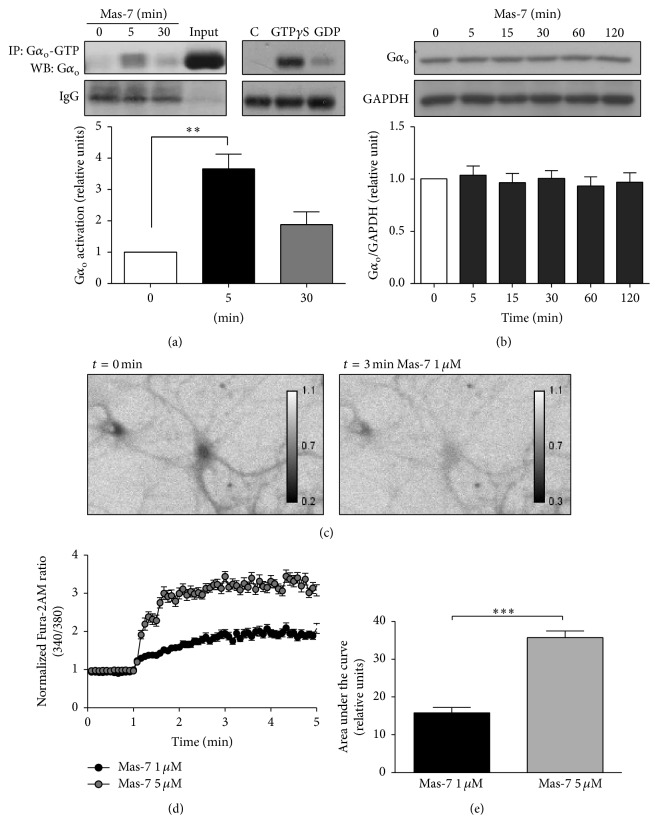
(a) Left panel, 14 DIV hippocampal neurons were stimulated with 1 μM Mas-7 for 0, 5, or 30 min. The neurons were lysed and incubated with anti-Gα o-GTP for 2 h and then analyzed by immunoblotting using an anti-Gα o antibody (n = 4). The input lane corresponds to a lysate sample before the immunoprecipitation. ∗∗ p < 0.01. Right panel, lysates from untreated (control) hippocampal neurons were incubated with GTPγS as a positive control or with GDP as a negative control for 90 min at RT. Then, the Gα o-GTP was immunoprecipitated and analyzed by western blotting to determine the total level of Gα o. The IgG band shows that an equal amount of antibody was used for the immunoprecipitation. (b) Representative western blot and quantification of the total level of Gα o in 14 DIV neurons incubated for different periods of time with 1 μM Mas-7. GAPDH was used as a loading control (n = 4). (c) Ratio images (340/380) of the Fura-2AM probe from hippocampal neurons under basal conditions (t = 0) or after 3 min of 1 μM Mas-7 treatment. (d) Quantification of measurements of the intracellular Ca2+ increase in hippocampal neurons bathed in a Ca2+-free solution with different concentrations of Mas-7 (n = 3, 70–79 neurons, each condition). (e) Area under the curve of the Ca2+ increase after Mas-7 treatment. ∗∗∗ p < 0.001.
2.10. Gαo Activation Assay
The activity of Gao was determined using Gαo Activation Assay Kit (NewEast Biosciences, Wuhan, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
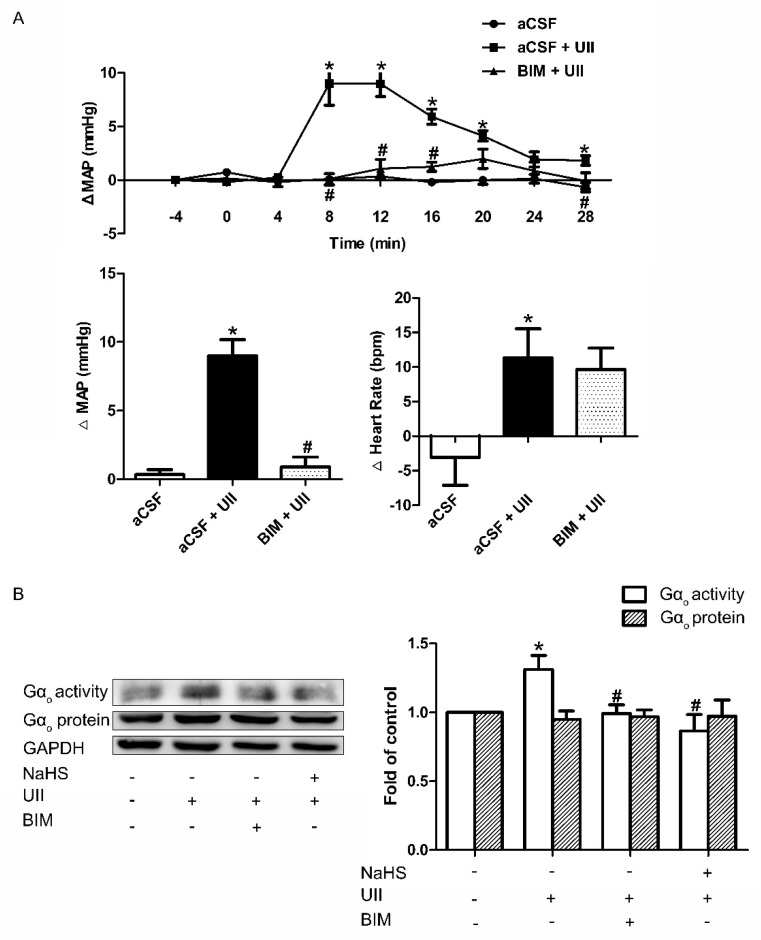
Inhibitory role of NaHS on UII−induced Gαo activation. Time course of MAP and the maximal changes in MAP and HR in response to microinjection of aCSF, aCSF + UII, or BIM + UII into the RVLM of SD rats
(A). The change in the activity and protein level of Gαo after pretreatment with NaHS or BIM for 30 min before UII was used (B). Densitometric analysis of the viability of Gαo (B). Mean ± SEM. n = 6. * p < 0.05 vs. aCSF group; # p < 0.05 vs. aCSF + UII group.
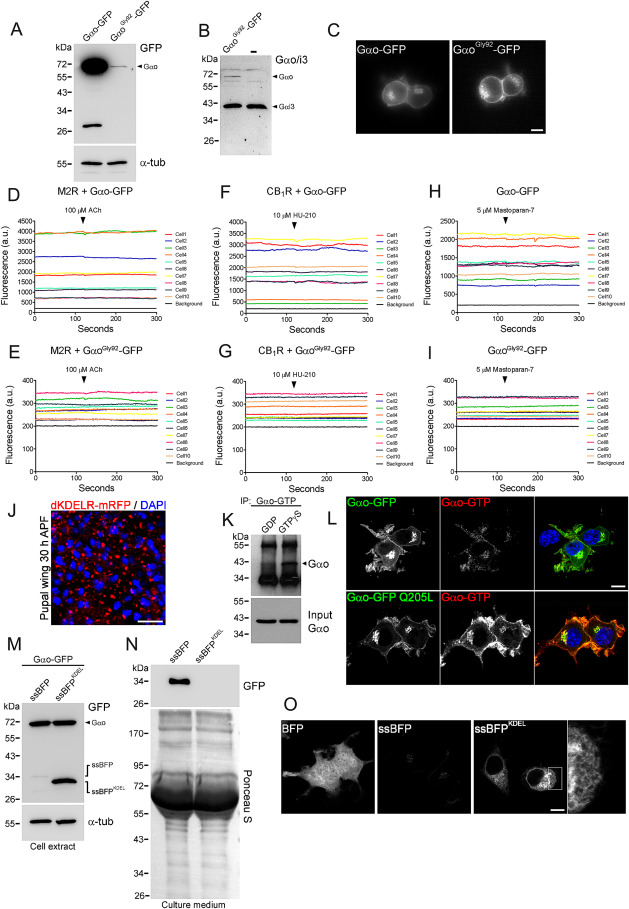
Activation of Gαo by KDELR
Figure S6 Gαo Does Not Translocate From the PM to the Golgi upon Activation, Related to Figures 5 and 6
Activation of Gαo by KDELR
Figure S7 KDELR Activates Gαo at the Golgi
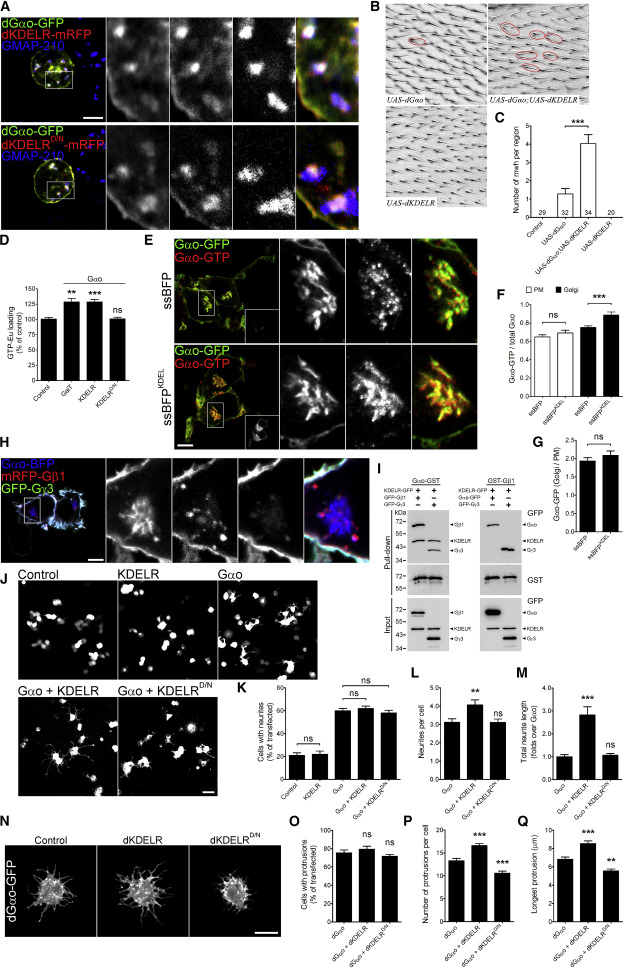
Activation of Gαo by KDELR
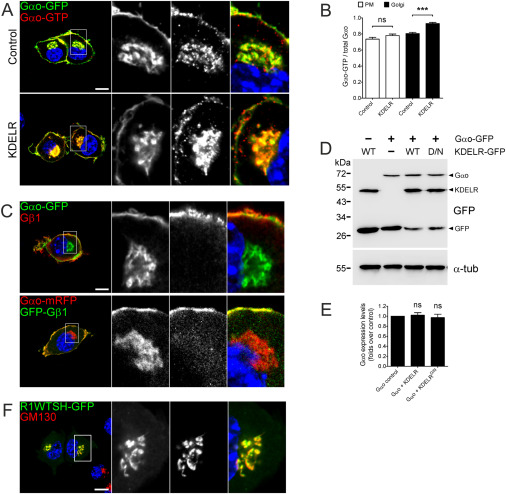
(E–G) Stimulation of KDELR activates Gαo in N2a cells (E). ssBFPKDEL but not control ssBFP stimulates endogenous KDELR. Activated Gαo is detected by Abs against Gαo-GTP. Marked regions are zoomed-in. Mean fluorescence intensity ratios of active versus total Gαo calculated at the PM and Golgi (F) and of total Gαo-GFP at the Golgi versus PM (G). Scale bar, 10 μm.

Immunoprecipitation of Gαi/o Proteins
We used the Gαo (80901) and Gαi (80301) activation assay kits from New East Biosciences. The cultured hippocampal neurons were seeded at a density of 900,000 cells/well at DIV 14 and were treated with Wnt-5a (300 ng/ml). After treatment, cells were lysed, and the amount of protein was quantified. The same amount of protein was used in each condition for the immunoprecipitation (400 μg) with the specific antibodies that recognize the GTP-bound Gαo or the GTP-bound Gαi proteins according to the manufacturer’s recommended protocol. GTPγS was used as a positive control and was added to the neuronal lysate and incubated for 90 min at room temperature before immunoprecipitation. The total level of protein was detected by immunoblot with the mouse anti-Gαo (1:1000) or mouse anti-Gαi (1:1000) antibodies from the activation kits from New East Bioscience.
For immunoprecipitation of total Gαo hippocampal cultured neurons were seeded at a density of 600,000 cells/well. The neurons were treated with vehicle or Wnt-5a and then lysed. After protein quantification, 400 μg of protein was incubated with 5 μg/ml of mouse anti-Gαo (sc-13532; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and 20 μl of agarose beads for 1 h at 4 °C with orbital rotation. The 10% of the sample was used as input. Next, the lysates were washed three times and suspended in 20 μl of Laemmli 2× loading buffer. The samples were analyzed by immunoblotting with rabbit anti-Gαo, goat anti-FZD9, and rabbit anti-Gβ1–5 antibodies.
Wnt-5a increases the GDP/GTP exchange of the Gαo subunit, and FZD9 is associated with Gαo in DIV 14 hippocampal neurons.
A, hippocampal neurons were stimulated with recombinant Wnt-5a for the indicated lengths of time. The lysates were incubated with specific antibodies that recognize Gαo-GTP or Gαi-GTP. As a positive control, untreated hippocampal neuron lysates were incubated with GTPγS for 90 min at room temperature and then incubated with the antibody. The lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with antibodies that recognize the total levels of Gαo or Gαi (n = 3). The IgG band shows that equal amounts of the Gαo/i-GTP antibodies were used for immunoprecipitation. Left panel, representative blot images. Right panel, blot quantifications. B, DIV 13 or 14 neurons were treated or not with Wnt-5a (30 min), and the lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Gαo antibody and immunoblotted with anti-FZD9 and anti-Gβ1–5 (this antibody labels all five Gβ isoforms) (n = 4) in the same membrane. Left panel, representative blot images. Right panel, blot quantifications. **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05. No Ab, no antibody was added; WB, Western blotting; IP, immunoprecipitation.



