CTC-BIOPSY®-A10
Automatic Circulating Tumor Cell Separator
Circulating Tumor Cell Separator
Based on the physical differences such as size, deformability, and fluid dynamics between Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs, 1 ctc per ml blood) and blood cells, the whole blood is filtered through patented nano-microsieve membrane and then CTCs with Cell diameter over 15 µm are captured and enriched on the membrane.
Cat. #: CTC-BIOPSY-A10
Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) detection offers advantages such as non-invasive, real-time monitoring. It serves as a powerful tool for guiding personalized treatment in breast cancer patients. CTC testing can replace or complement tissue samples for pathological diagnosis, prognosis assessment, and subtype analysis. Additionally, dynamic CTC monitoring aids in disease progression evaluation and treatment efficacy assessment. CTC counts hold prognostic value for both early-stage and metastatic breast cancer. Notably, in early-stage breast cancer, a CTC count ≥1 signifies the presence of minimal residual disease (MRD) or indicates poorer prognosis.
CTCs can be thought of as a liquid biopsy from the blood. The clinical applications of CTCs include selection and monitoring of therapeutic regimens; and drug target applications.
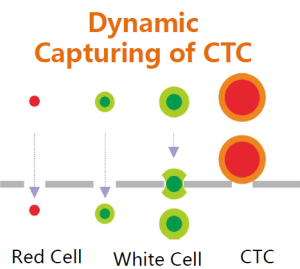
Utilizing suction filtration technique to separate CTC and CTM from the red blood cells in the whole blood. CTC and CTM are retained on the membrane.

The membrane is nano-microsieve with 13 mm in diameter. It has 160,000 micropores. The pore size is uniform (8 um), and the inter-pore distance is also uniform (25 um). It allows for efficient enrichment of CTCs, making CTCs visible under a regular microscope.
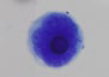
The micro sieve membrane is second-generation nano polymer material. It is resistance to various staining reagents with good light transmission. It allows us to directly observe the CTC under microscope.

High automation, 10 mins to complete CTC capture and enrichment of 5ml of the whole blood .
Nano-microscreen technology, no reliance on specific cell marker, suitable for all types of tumors.
Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC)
CTCs are found in the blood as either single cells, bound together in tight ‘microclusters’, and/or clustered together with immune cell
Circulating Tumor Microemboli (CTM)
Have at least 3 CTCs
Play an important role in tumor metastasis. The metastasis risk increases by 23-50 times.
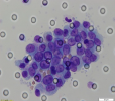
CTC Neutrophil Clusters (Neutrophil CTM)
CTC neutrophil clusters, representing a critical weakness in the metastatic process, the link between neutrophils and CTC drives the progress of cell cycle in the blood flow and expands the metastatic potential of CTC.
The survival period decreases by 5 times.
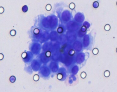
Tumor Metastasis Risk: CTC < CTM < Neutrophil CTM
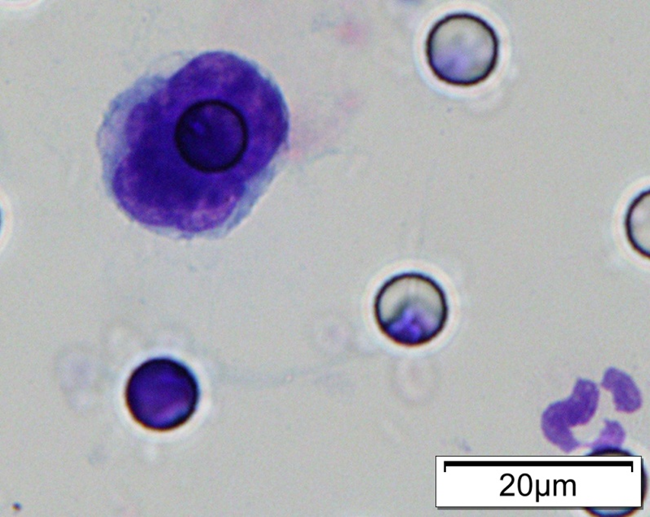
1. Cell diameter (longest side) > 15µm;
2. Nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio (NCR) > 0.8;
3. Abnormal nuclear morphology, such as lobulated or mulberry-like nuclei;
4. Hyperchromatic and unevenly stained nuclei;
5. Thickened nuclear membrane with indentations or folds, resulting in an irregular nuclear shape;
6. Presence of giant nucleoli;
※ A single CTC (Circulating Tumor Cell) is defined as meeting 4 or more criteria.
※ A cluster of 3 or more CTCs is referred to as a CTM (Circulating Tumor Microemboli).
※ When a CTM combines with a neutrophil, it is referred to as a Neutrophil CTM. Complying with 4 or more items is considered a single CTC.
CTC pathology detection is the gold standard – classic technology
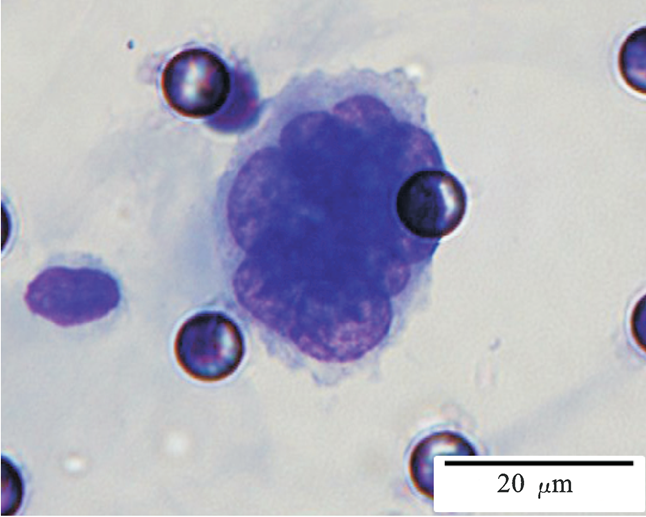
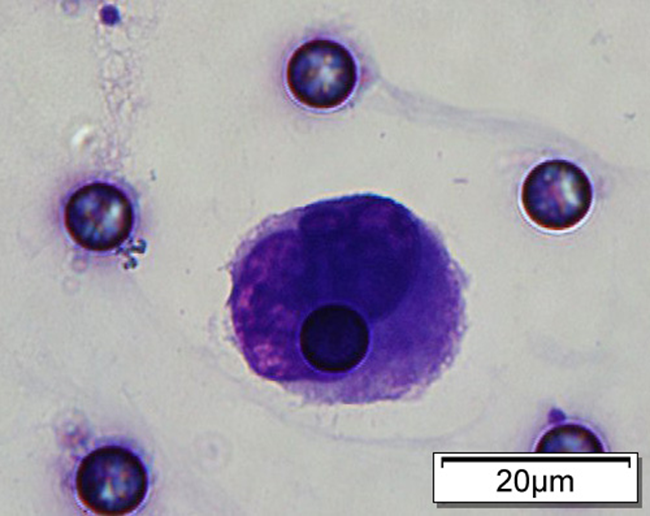
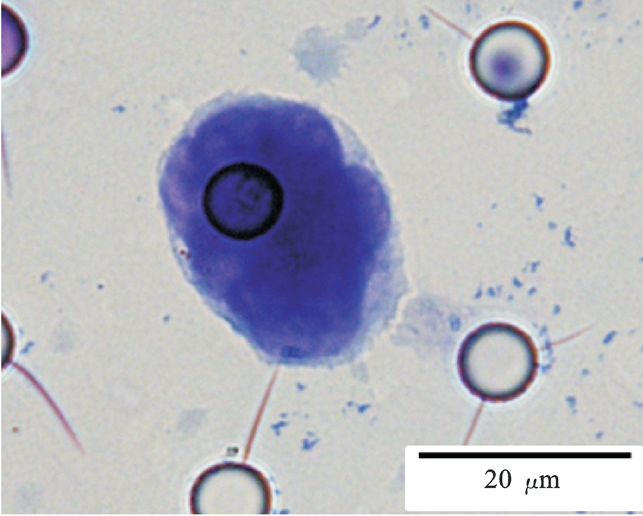
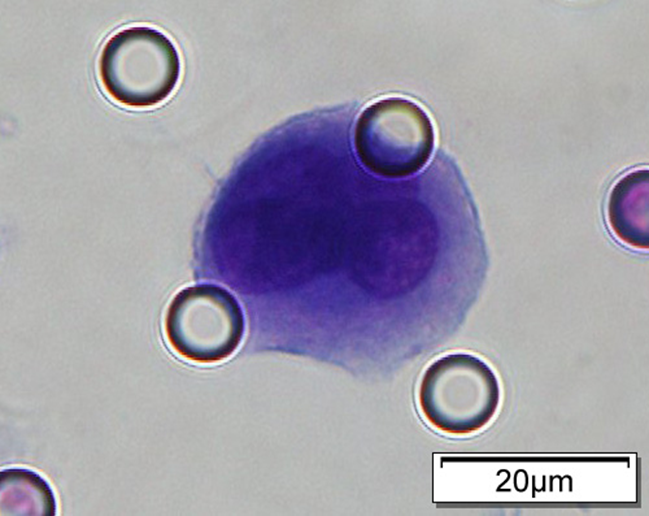
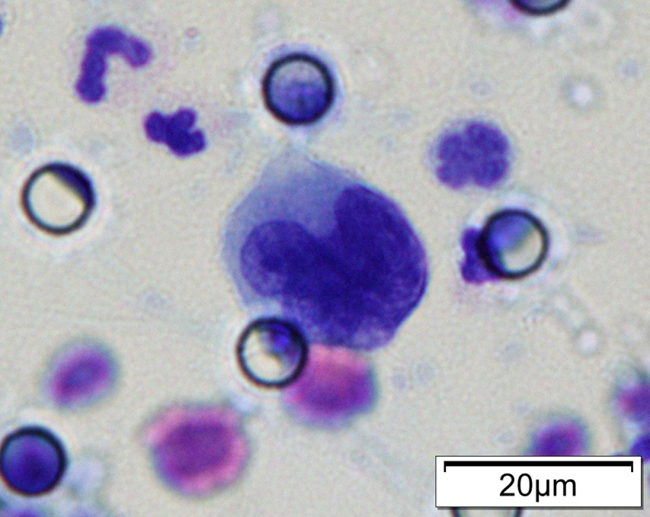
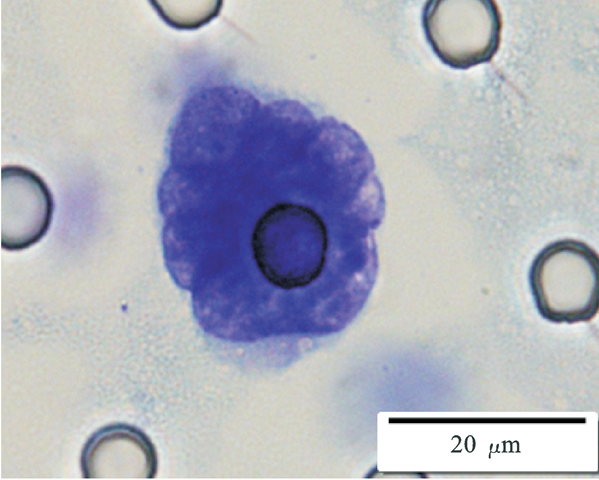
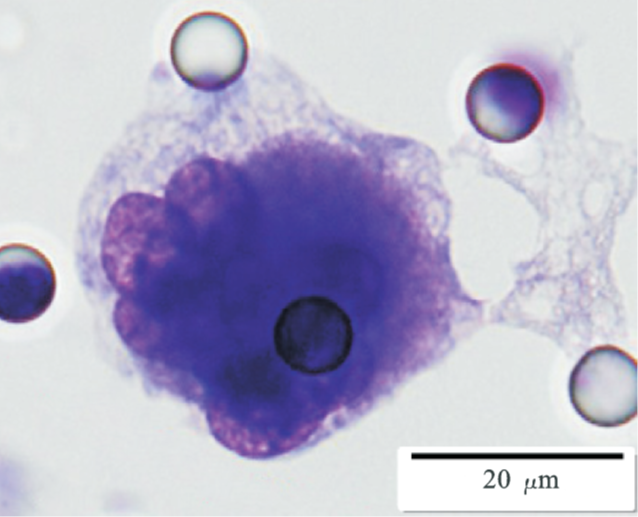
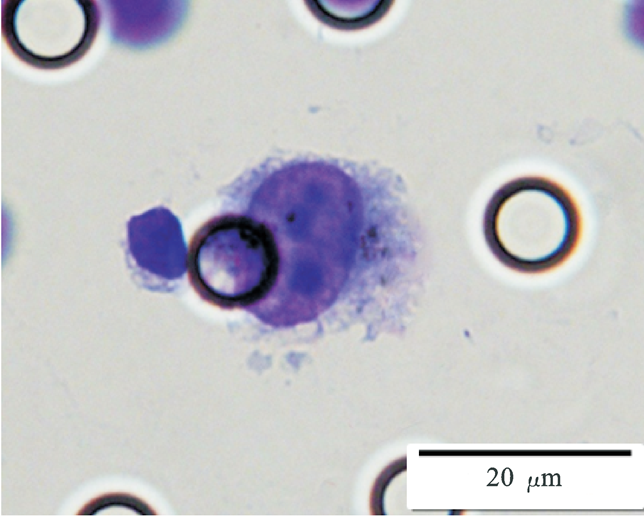
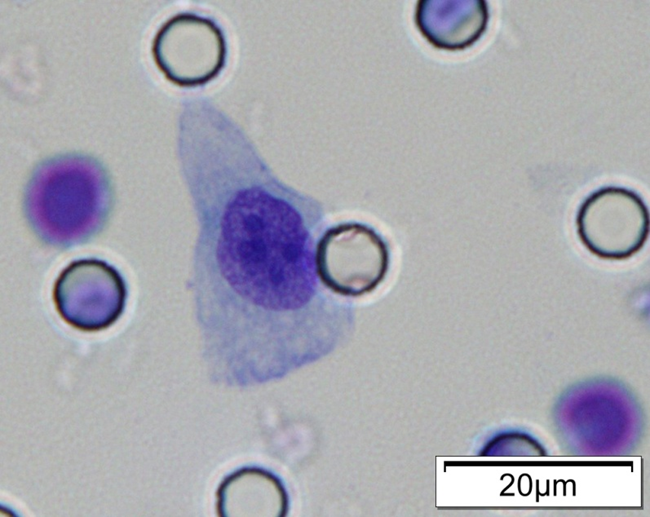
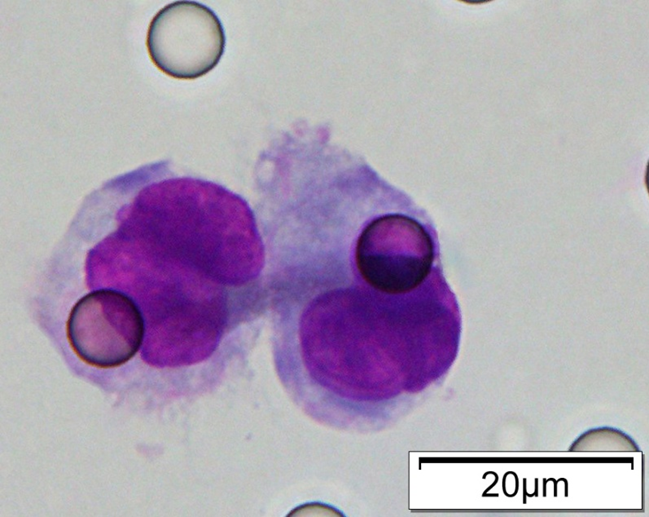
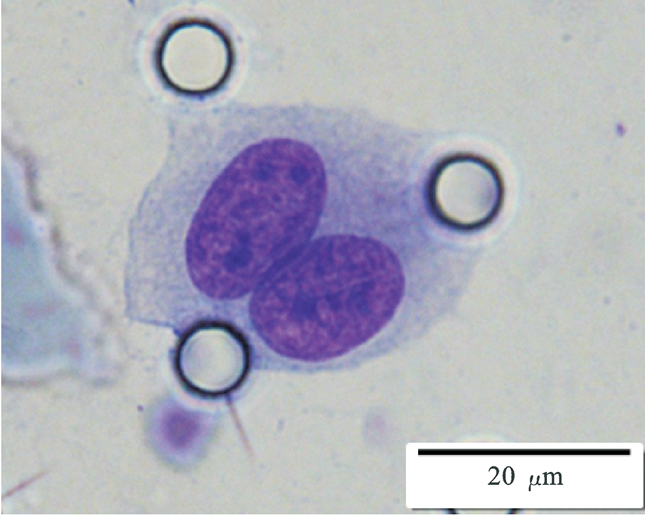
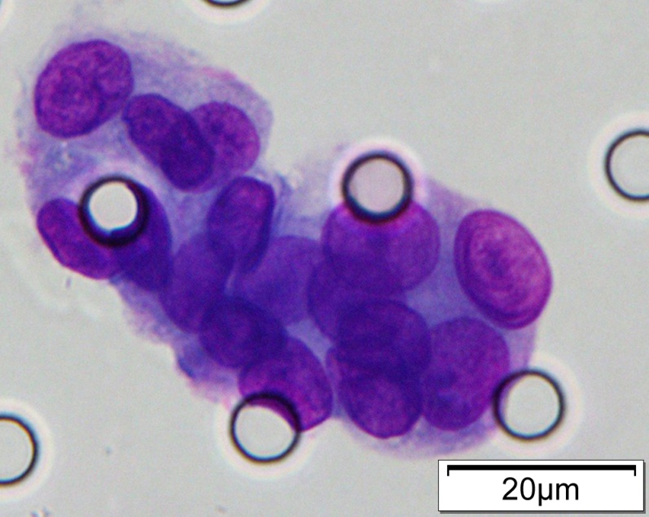
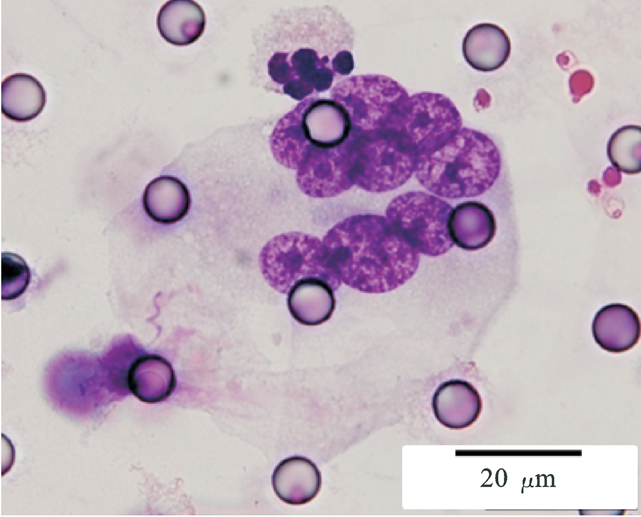
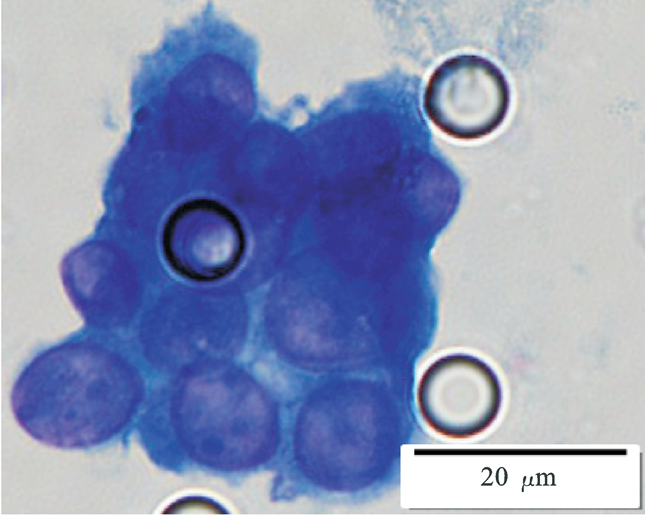
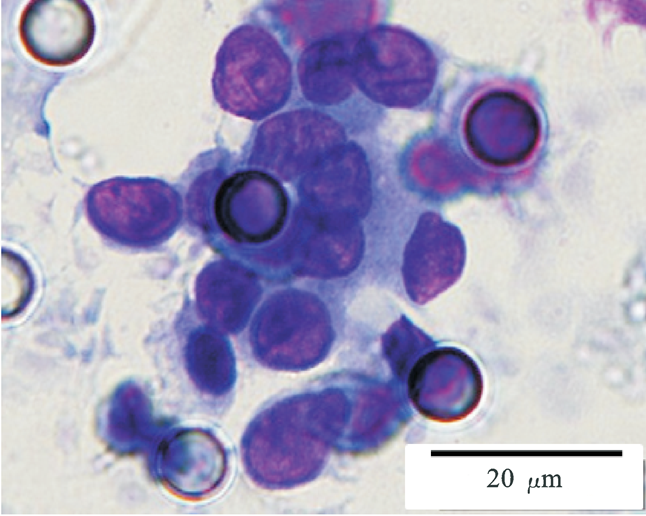
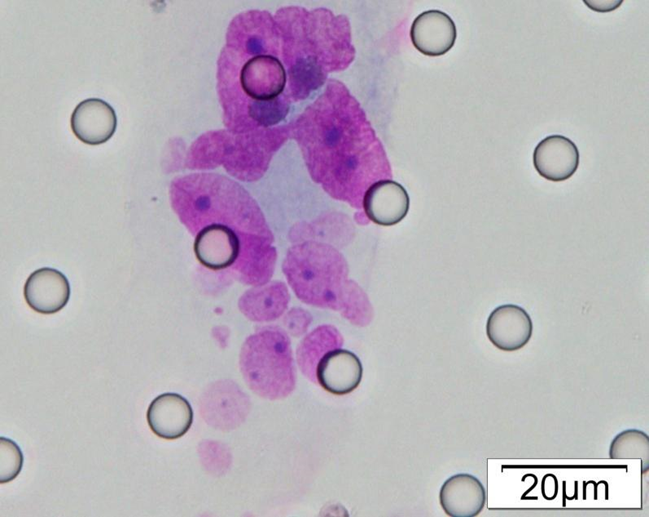
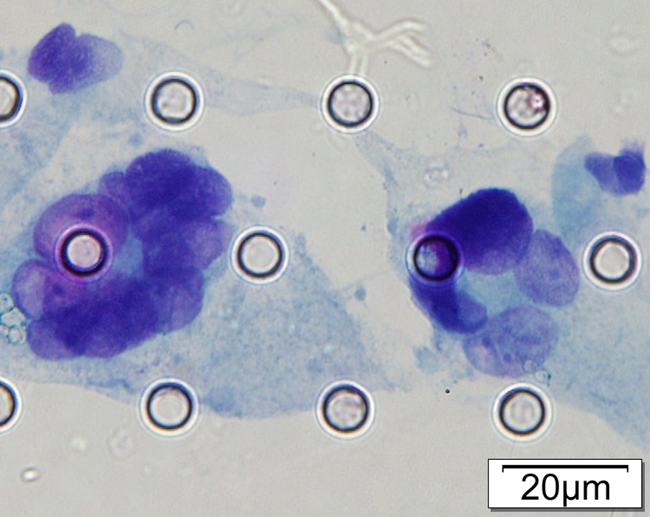
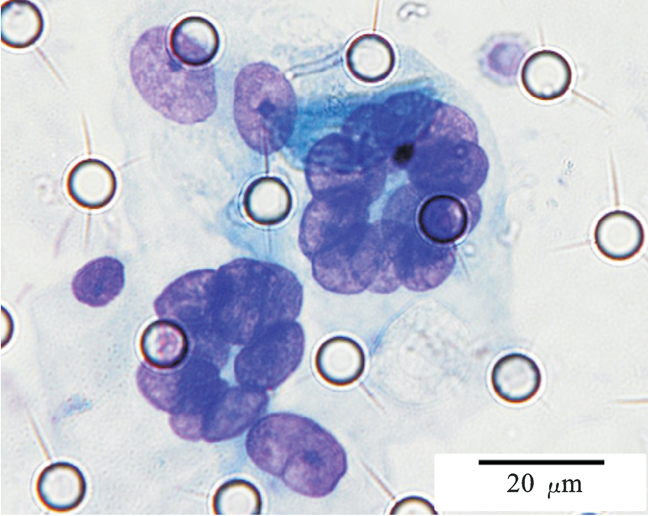
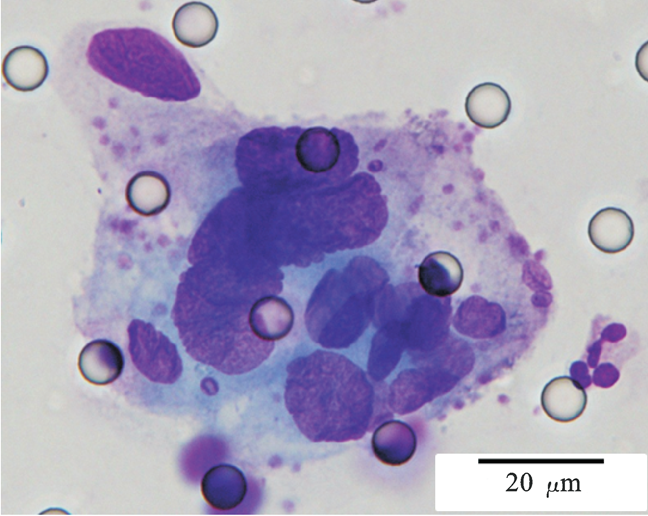
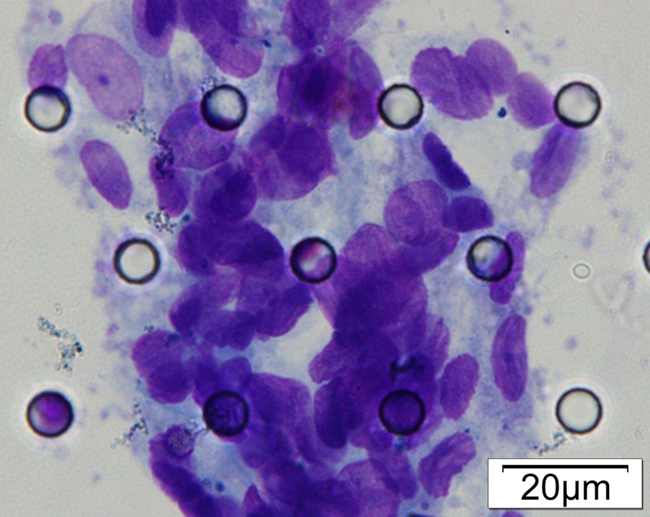
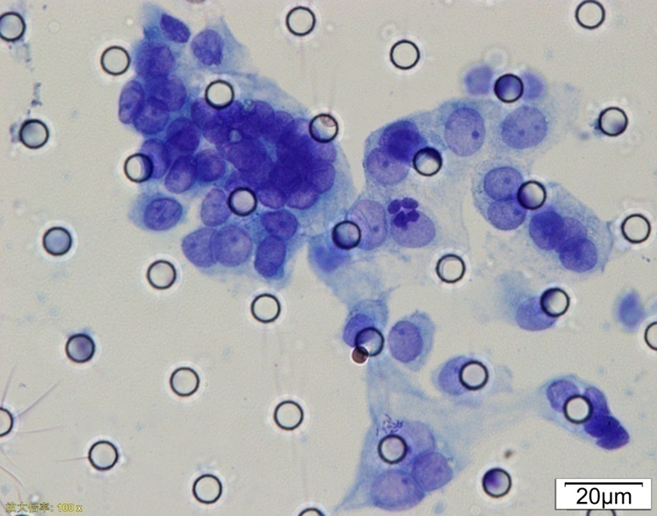
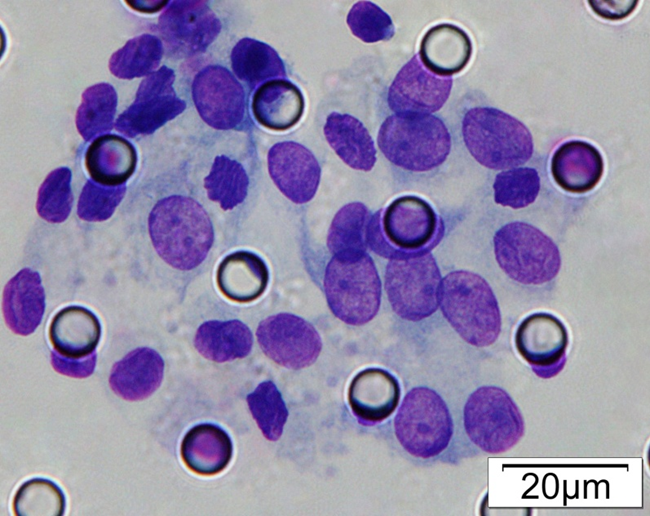
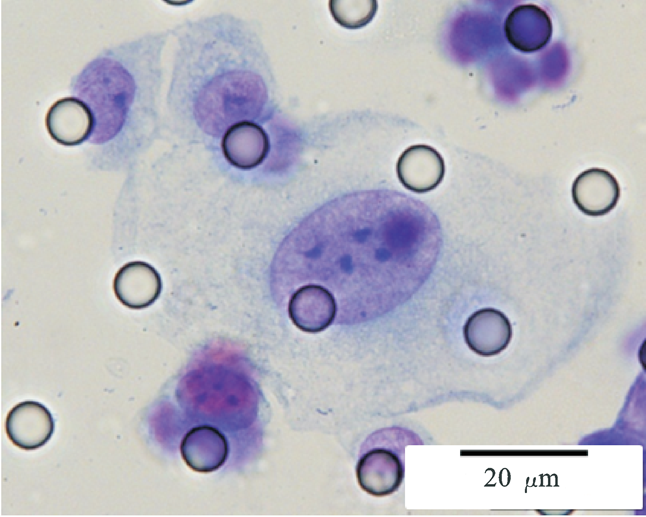
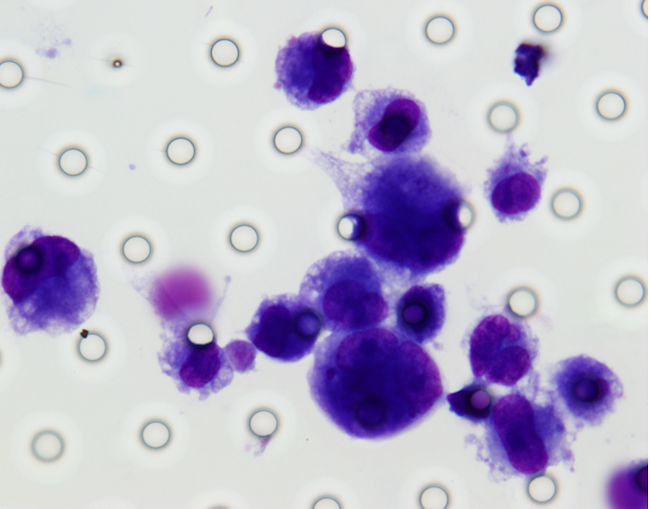
Images of CTC or CTM from invasive adenocarcinoma, prostate cancer, right lung cancer, lobar invasive adenocarcinoma, adenocarcinoma of gastric fundus, kidney cancer, colon cancer,ulcerative gastric adenocarcinoma, moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma of the rectum, stomach cancer, rectal adenocarcinoma and breast cancer etc.
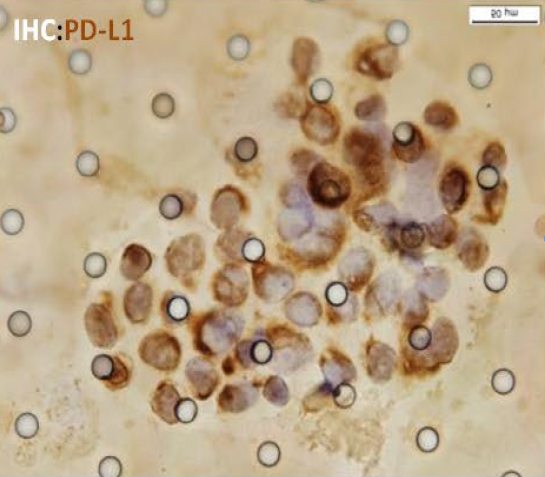
IHC
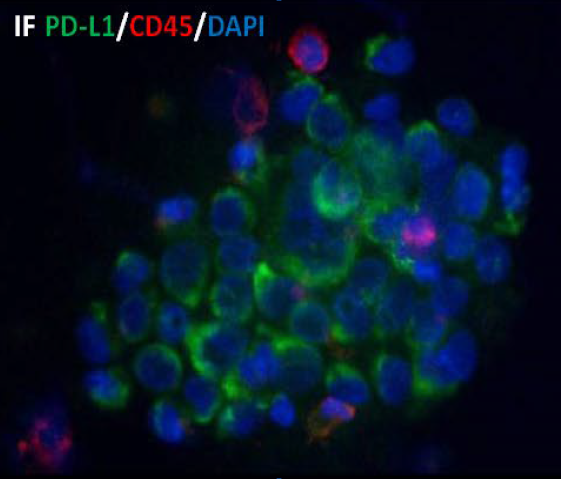
IF
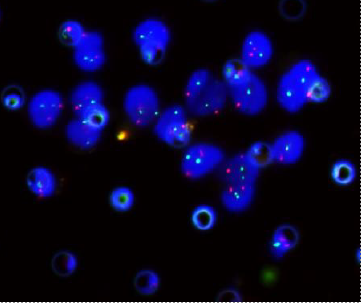
FISH
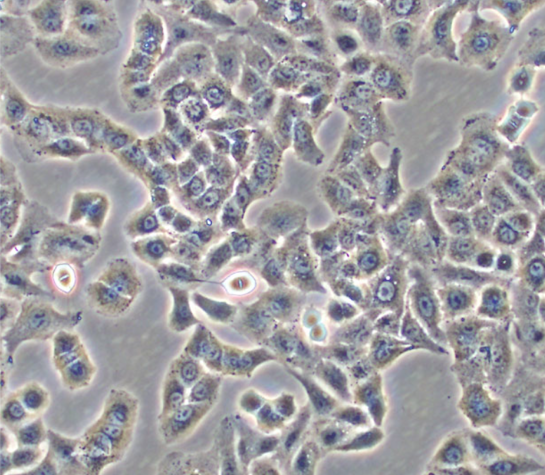
Cell Culture
High automation, 10 mins to complete CTC capture and enrichment of 5ml of whole blood .
Nano-microscreen technology, no reliance on specific cell marker, suitable for all types of tumors.
No lysis of red blood cells or pre-centrifugation to preserve the CTM intact, direct observation under microscope.
Autonomous downstream analyses, such as IF, IHC, FISH and sequencing to meet the requirements of clinical research.
Optimized isolation technology by size of epithelial tumor cells (ISET) can accurately and reliably capture abnormal cells in blood, providing a efficient solution for tumor screening.
■ High-risk Tumor screening
■ Companion Diagnosis ■ Early Warning

Automated Device
High-precision peristaltic pump with negative pressure
High-precision pressure sensor
Automatic control and simulation
Easy Operation
Friendly operation interface
Sorting of samples with one click
Real-time display of blood sample processing
Authoritative Identification
Norms for identification of cell morphology
formulated by authoritative pathology experts
Quick Separation
No reliance on cell marker for separation
Single sample isolation time <10 mins
ISET technology uses the size and deformability of tumor cells to achieve separation, then use cell morphology for identification.
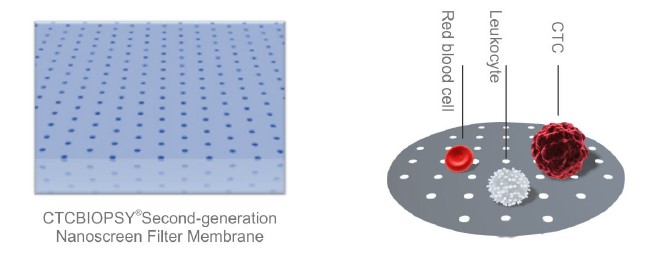
■ With good light transmission, second-generation nano polymer material is resistance to various staining reagents, allowing direct observation of cells in visible light.
■ Nano-microsieve technology broke the foreign monoply, high-precision lithography machine for laser lithography.
■ 13mm micro sieve membrane has 160,000 nano micro sieves with an aperture of 8um to maximize the sorting of blood cells and tumor cell enrichment.
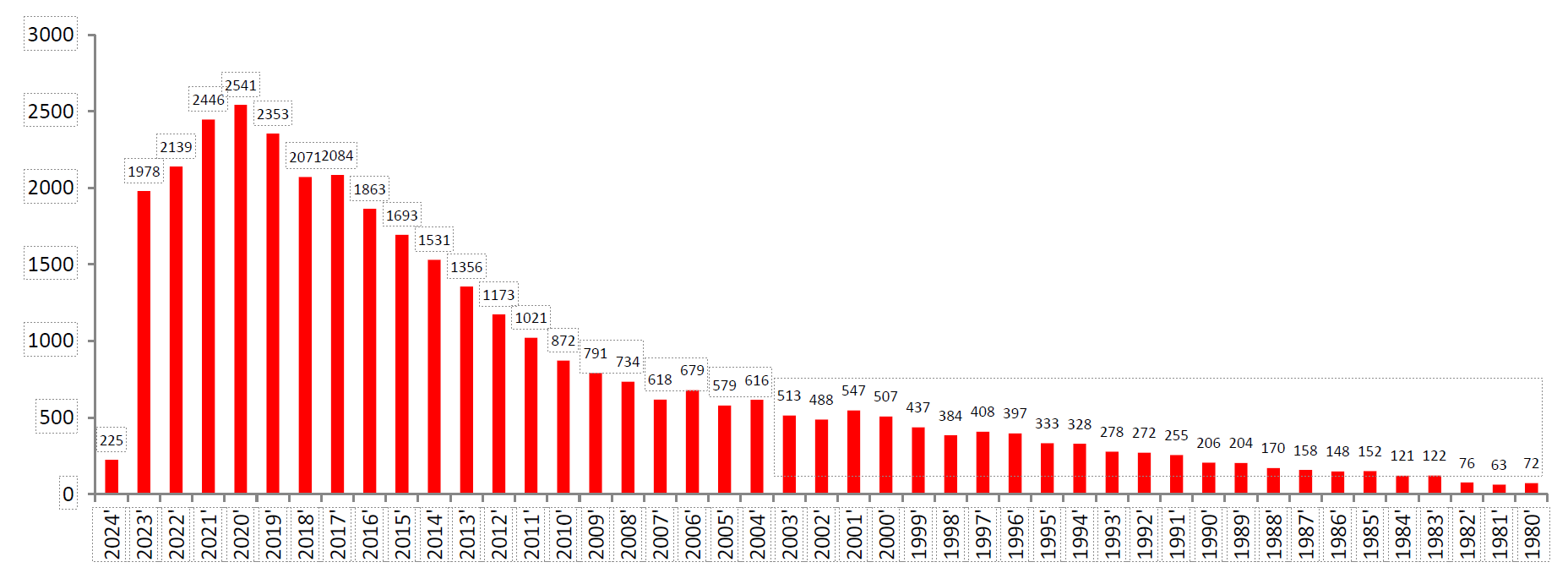
CTC detection data of the CTC-BIOPSY® system in 2018-2020 showed an average CTC detection rate for each tumor is 80.90% ,CTM (Circulating Tumor Microemboli) detection rate is 12.52%, and the ratio of CTM to total CTC detection was consistent with study data from Nature in 2019.
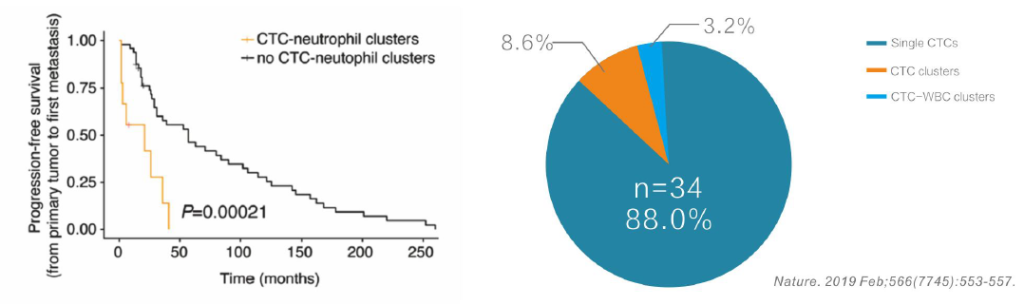
Partial Detection Data of CTC and CTM from 2018 to 2020:
Long non‐coding RNAFOXD1‐AS1 modulated CTCs epithelial‐mesenchymal transition and immune escape in hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro by sponging miR‐615‐3p
J Hematol Oncol., 2024, PMID: 38517478Longitudinal Change of Circulating Tumor Cells During Chemoradiation and Its Correlation with Prognosis in Advanced Nonsmall-Cell Lung Cancer Patients
Cancer Biother Radiopharm., 2023, PMID: 33481670Circulating tumour cell combined with DNA methylation for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma
Front Genet., 2022, PMID: 36479252Detection of circulating tumor cells and evaluation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition patterns of circulating tumor cells in ovarian cancer
Transl Cancer Res., 2022, PMID: 36093536Circulating Tumor Cells and Breast Cancer Metastasis: From Enumeration to Somatic Mutational Profile
Transl Cancer Res., 2022, PMID: 36294386Ionizing Radiation-Induced Tumor Cell-Derived Microparticles Prevent Lung Metastasis by Remodeling the Pulmonary Immune Microenvironment
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. , 2022, PMID: 35840114A novel combined fluorescent probe staining method for circulating tumor cell identification
Ann Transl Med. , 2022, PMID: 35282100Identifying circulating glioma cells and their clusters as diagnostic markers by a novel detection platform
Clin Transl Med., 2021, PMID: 33634975Comparison of CellSearch and Circulating Tumor Cells (CTC)-Biopsy Systems in Detecting Peripheral Blood Circulating Tumor Cells in Patients with Gastric Cancer
Med Sci Monit., 2021, PMID: 33408319Clearance of circulating tumor DNA in a high-risk stage-IV rectal carcinoma patient with synchronous liver metastases after conversion surgery is correlated with pathologic complete response
Ther Adv Gastrointest Endosc., 2021, PMID: 34124665EMT‐cancer cells‐derived exosomal miR‐27b‐3p promotes circulating tumour cells‐mediated metastasis by modulating vascular permeability in colorectal cancer
Clin Transl Med., 2021, PMID: 34936736Dynamic evaluation of mesenchymal circulating tumor cells in patients with colorectal cancer: Clinical associations and prognostic value
Oncol Rep., 2020, PMID: 32627039Circulating tumor cells in whole process management of gastrointestinal stromal tumor in a real-life setting
Saudi J Gastroenterol., 2020, PMID: 32386192Wnt5a-induced M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages via IL-10 promotes colorectal cancer progression
Cell Commun Signal., 2020, PMID: 32228612Isolation of circulating tumor cells in patients undergoing surgery for esophageal cancer and a specific confirmation method
Oncol Lett. 2019, PMID: 30881502Circulating Tumor Cells in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Current Status and Future Perspectives
Front Oncol. 2019, PMID: 31921680Combined Features Based on Preoperative Controlling Nutritional Status Score and Circulating Tumour Cell Status Predict Prognosis for Colorectal Cancer Patients Treated with Curative Resection
Int J Biol Sci., 2019, PMID: 31223290Crosstalk between cancer cells and tumor associated macrophages is required for mesenchymal circulating tumor cell-mediated colorectal cancer metastasis
Mol Cancer. 2019, PMID: 30927925miR-195-5p/NOTCH2-mediated EMT modulates IL-4 secretion in colorectal cancer to affect M2-like TAM polarization
J Hematol Oncol., 2019, PMID: 30808369KIAA1199 promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer cells via microtubule destabilization regulated by a PP2A/stathmin pathway
Oncogene., 2019, PMID: 30202098Elevated CD163+/CD68+ Ratio at Tumor Invasive Front is Closely Associated with Aggressive Phenotype and Poor Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer
Int J Biol Sci., 2019, PMID: 31182919Wedge-shaped microfluidic chip for circulating tumor cells isolation and its clinical significance in gastric cancer
J Transl Med., 2018, PMID: 29792200Prognostic value of pre- and post-operative circulating tumor cells detection in colorectal cancer patients treated with curative resection: a prospective cohort study based on ISET device
Cancer Manag Res., 2018, PMID: 30323669Highly Efficient Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells Using a Simple Wedge-Shaped Microfluidic Device
IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. , 2018, PMID: 30307854Down-regulation of KIAA1199/CEMIP by miR-216a suppresses tumor invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer
Int J Cancer., 2017, PMID: 28213952- Citations Ranked by Product
- 1. 26903 Rac1-GTP
- 2. 26904 RhoA-GTP
- 3. 26905 Cdc42-GTP
- 4. 80203 cAMP EIA Kit – No Acetylation
- 5. 80103 cGMP EIA Kit – No Acetylation
- 7. 26039 BRAF(V600E)
- 6. 26901 Gαi-GTP
- 8. 26909 Ras-GTP
- 9. 26911 Rab5-GTP
- 10. 26163 IDH2(R172K)
- 11. 26919 Rab11-GTP
- 12. 26910 Reb-GTP
- 13. 26036 Ras(G13D)
A Solution for Real-time Tumor Monitoring
Convenient · Efficient · Accurate
CTC-BIOPSY®-A10