About NewEast
NewEast Biosciences pioneered the research and development of the antibodies for GTPases and mutated Oncogene ten years ago. GTPases involve (1) signal transduction in response to activation of cell surface receptors, including transmembrane receptors such as those mediating taste, smell and vision, (2) protein biosynthesis at the ribosome, (3) regulation of cell differentiation, proliferation, division and movement, (4) translocation of proteins through membranes, (5) transport of vesicles within the cell, and vesicle-mediated secretion and uptake, through GTPase control of vesicle coat assembly. An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer.
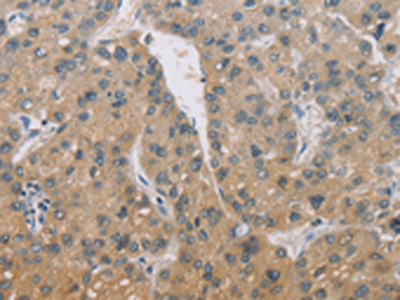
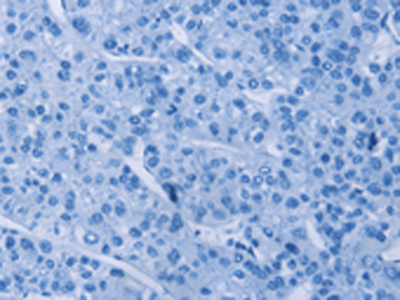
We offer three unique categories of antibodies, which (1) recognize only the active configuration of GTPase (not the inactive one), (2) mutated Oncogene (not mild type) and (3) have super affinity for cAMP and cGMP (no acetylation required). We have over one thousand peer reviewed articles cited our products.

Citations on Top 50 Journals
(Google Scholar)
- Rank Journal Name
- 1. Nature
- 7. Nature Communications
- 8. Cell
- 13. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
- 18. Nucleic Acids Research
- 20. Nature Medicine
- 25. ACS Nano
- 29. Scientific Reports
- 33. PLoS ONE
- 34. Science Advances
- 37. Nature Genetics
- 41. International Journal of Molecular Sciences
- 49. Frontiers in Immunology