| Cat.#: N225483 |
| Product Name: Anti-Phospho-PKA alpha/beta/gamma (Thr197) Rabbit pAb |
| Synonyms: PRKACA; PKACA; cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha; PKA C-alpha; PRKACB; cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit beta; PKA C-beta; PRKACG; cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit gamma; PKA C-gamma |
| UNIPROT ID: P17612/P22694/P22612 |
| Background: PRKACA (protein kinase cAMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha) encodes one of the catalytic subunits of protein kinase A, which exists as a tetrameric holoenzyme with two regulatory subunits and two catalytic subunits, in its inactive form. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Four different regulatory subunits and three catalytic subunits have been identified in humans. cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of proteins by protein kinase A is important to many cellular processes, including differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. Constitutive activation of this gene caused either by somatic mutations, or genomic duplications of regions that include this gene, have been associated with hyperplasias and adenomas of the adrenal cortex and are linked to corticotropin-independent Cushing’s syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Tissue-specific isoforms that differ at the N-terminus have been described, and these isoforms may differ in the post-translational modifications that occur at the N-terminus of some isoforms. |
| Immunogen: The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human PKA CAT around the phosphorylation site of Thr197. AA range:166-215 |
| Applications: WB,IHC-F,IHC-P,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| Recommended Dilutions: WB: 1/500-1/1000 IHC: 1/50-1/100 IF: 1/50-1/200 ELISA: 1/10000 |
| Host Species: Rabbit |
| Clonality: Rabbit Polyclonal |
| Clone ID: – |
| MW: Calculated MW: 40 kDa; Observed MW: 40 kDa |
| Isotype: IgG |
| Purification: Affinity Chromatography |
| Species Reactivity: Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Conjugation: Unconjugated |
| Modification: Phosphorylated |
| Constituents: PBS (without Mg2+ and Ca2+), pH 7.3 containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide |
| Research Areas: Signal Transduction |
| Storage & Shipping: Store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing |
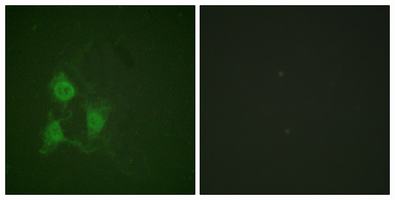
Immunofluorescence analysis of Phospho-PKA alpha/beta/gamma (Thr197) in A549 using Phospho-PKA alpha/beta/gamma (Thr197) antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the Phospho- peptide. | 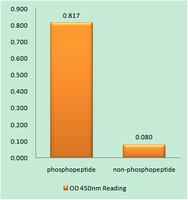
EnzymeLinked Immunosorbent Assay (Phospho-ELISA) for Immunogen Phospho-peptide (Phospho-left) and NonPhospho-peptide (Phospho-right), using PKA CAT (Phospho-Thr19antibody | 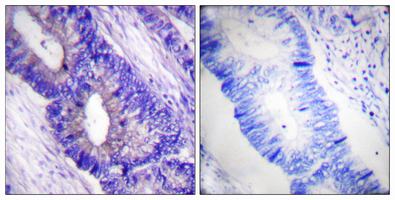
Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded Human colon carcinoma using Phospho-PKA alpha/beta/gamma (Thr197) antibody. High-pressure and temperature Sodium Citrate pH 6.0 was used for antigen retrieval.Sample with blocking peptide on the right. | 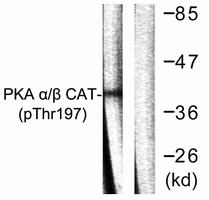
Western blot analysis of Phospho-PKA alpha/beta/gamma (Thr197) in mouse brain lysates using Phospho-PKA alpha/beta/gamma (Thr197) antibody.The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide. |
|