| Cat.#: 28229 |
| Product Name: Anti-CD5L(DMC441) IgG1 Chimeric Monoclonal Antibody |
| Synonyms: AIM; API6; CT-2; hAIM; PRO229; SP-ALPHA; Spalpha |
| Description: Anti-CD5L antibody(DMC441) IgG1 Chimeric Monoclonal Antibody |
| Background: Secreted protein that acts as a key regulator of lipid synthesis: mainly expressed by macrophages in lymphoid and inflamed tissues and regulates mechanisms in inflammatory responses; such as infection or atherosclerosis. Able to inhibit lipid droplet size in adipocytes. Following incorporation into mature adipocytes via CD36-mediated endocytosis; associates with cytosolic FASN; inhibiting fatty acid synthase activity and leading to lipolysis; the degradation of triacylglycerols into glycerol and free fatty acids (FFA). CD5L-induced lipolysis occurs with progression of obesity: participates in obesity-associated inflammation following recruitment of inflammatory macrophages into adipose tissues; a cause of insulin resistance and obesity-related metabolic disease. Regulation of intracellular lipids mediated by CD5L has a direct effect on transcription regulation mediated by nuclear receptors ROR-gamma (RORC). Acts as a key regulator of metabolic switch in T-helper Th17 cells. Regulates the expression of pro-inflammatory genes in Th17 cells by altering the lipid content and limiting synthesis of cholesterol ligand of RORC; the master transcription factor of Th17-cell differentiation. CD5L is mainly present in non-pathogenic Th17 cells; where it decreases the content of polyunsaturated fatty acyls (PUFA); affecting two metabolic proteins MSMO1 and CYP51A1; which synthesize ligands of RORC; limiting RORC activity and expression of pro-inflammatory genes. Participates in obesity-associated autoimmunity via its association with IgM; interfering with the binding of IgM to Fcalpha:mu receptor and enhancing the development of long-lived plasma cells that produce high-affinity IgG autoantibodies (By similarity). Also acts as an inhibitor of apoptosis in macrophages: promotes macrophage survival from the apoptotic effects of oxidized lipids in case of atherosclerosis (PubMed:24295828). Involved in early response to microbial infection against various pathogens by acting as a pattern recognition receptor and by promoting autophagy (PubMed:16030018; PubMed:24223991; PubMed:24583716; PubMed:25713983). |
| Applications: Flow Cyt |
| Recommended Dilutions: Flow Cyt 1:100 |
| Host Species: Rabbit |
| Isotype: Rabbit:Human Fc chimeric IgG1 |
| Purification: Purified from cell culture supernatant by affinity chromatography |
| Species Reactivity: Human CD5L |
| Constituents: Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 5 % – 8% trehalose is added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Storage & Shipping: Store at -20°C to -80°C for 12 months in lyophilized form. After reconstitution, if not intended for use within a month, aliquot and store at -80°C (Avoid repeated freezing and thawing). |
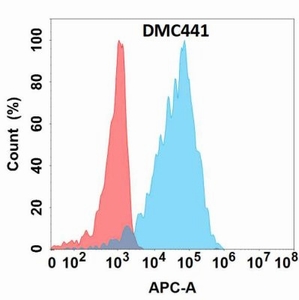
Figure 1. Flow cytometry analysis with Anti-CD5L (DMC441) on Expi293 cells transfected with human CD5L (Blue histogram) or Expi293 transfected with irrelevant protein (Red histogram). |