Product Description
Apolipoprotein A1 is the major protein component of serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL). It is produced in the liver and is involved in cholesteryl ester formation and cholesterol transport from tissues to the liver, which is thought to inhibit atherogenesis. The plasma concentration of Apolipoprotein A1 is one of the best indicators of susceptibility to cardiovascular disease.
NewEast Biosciences Human Apolipoprotein A1 ELISA Kit is a simple and fast sandwich enzyme immunoassay (EIA) for in vitro quantitative detection of human Apolipoprotein A1 proteins in urine, saliva, milk and cell culture samples.
Each kit provides sufficient quantities to perform 96 assays. It works for Apolipoprotein A1 of primates.
Assay Principle
With the NewEast Biosciences Human Apolipoprotein A1 Sandwich ELISA Assay system, mouse monoclonal antibodies generated against human Apolipoprotein A1, are pre-coated onto a 96-well plate and are used to capture human Apolipoprotein A1 from a sample. Captured human Apolipoprotein A1 is detected using human Apolipoprotein A specific rabbit polyclonal antibodies(biotin labeled)and streptavidin-conjugated poly-HRP.
After the addition of the substrate solutions, the amount of human Apolipoprotein A1 is determined. The standard curve demonstrates a direct relationship between Optical Density (OD) and human Apolipoprotein A1 concentration: i.e., the higher the OD the higher the human Apolipoprotein A concentration in the sample.
Kit Components
1. Mouse anti-Apolipoprotein A1 monoclonal antibody Coated microtiter plate (Catalog No.30501): One Plate of 96 Wells.
2. Assay/Diluent Buffer (Catalog No. 30403): One bottle of 30 mL of 100 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.2, 1% BSA, 0.1% Tween-20 and 0.02% Thimerosol.
3. Biotin labelled rabbit anti-Apolipoprotein A1 polyclonal antibody (Catalog No. 21113 -conjugated): One vial 15 µL
4. Streptavidin-conjugated poly-HRP (Catalog No. 29030)
5. 10X Wash Buffer Concentrate (Catalog No. 30106): One bottle of 15 mL phosphate buffered saline containing detergents.
6. ApoA1 Standard (Catalog No. 30502): One vial (10 µg) of human ApoA1 protein.
7. Substrate A (Catalog No. 30107): One vial 6 mL.
8. Substrate B (Catalog No. 30108): One vial 6 mL.
9. Stop Solution (Catalog No. 30110): One vial 12 mL. A solution of oxalic acid in water. Keep tightly capped.
Storage
Store all kit components at 4ºC until their expiration dates. Note: For long-term best results, store anti- Apolipoprotein A1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog No. 30501), human ApoA1 protein standard (Catalog No.30502) at -80℃upon receipt. Add 1 µL anti- Apolipoprotein A1 mouse monoclonal antibody into 2 mL diluent buffer and mix the solution gently before use. Please avoid repeated thawing and freezing after mixing.
Materials Needed but Not Supplied
1. Multi-channel or repeating pipettes
2. Pipettors & tips capable of accurately measuring 10-1000 µL
3. Graduated serological pipettes
4. 96-well microplate reader capable of measuring absorbance at 405 nm
5. Graph paper for manual plotting of data
6. 1.5 mL tubes
7. Mechanical vortex
8. Two1 litre containers
9. Plate shaker (optional)
10. Distilled or deionized water
Reagent Preparation
1. ApoA1 Standard Allow the Apolipoprotein A1 standard solution to warm to room temperature. Label 6 (or more) tubes #1 through #6. Pipet 100µL assay diluent into tube #1 and 300 µL assay diluent into tubes #2-6. Add 10 ug/ml Apolipoprotein A1 standard to tube #1. Vortex thoroughly. Add 100 µL of tube #1 to tube #2 and vortex thoroughly. Continue this for tubes #3 through #6.The concentration of Apolipoprotein A1 in tubes #1 through #6 will be 10, 5, 2.5, 1.25, 0.625, 0.3125 ug/ml, respectively. Diluted standards should be used within 30 minutes of preparation.
2. Biotin labelled rabbit anti-Apolipoprotein A1 polyclonal antibody Immediately before use, dilute Biotin-labelled rabbit anti-Apolipoprotein A1 polyclonal antibody 1:1000 with assay/diluent buffer as follows: For every 20 well strips, prepare 2 mL of diluted anti-Apolipoprotein A1 antibody by adding 2 µL of anti-Apolipoprotein A1 mouse monoclonal antibody to 1998 µL of assay/diluent buffer.
3. Streptavidin-conjugated poly-HRP Immediately before use, dilute the Streptavidin-conjugated poly-HRP 1:5,000 with ELISA Assay/Diluent buffer as follows: For each 50 well strips prepare 5 mL of diluted goat anti-rabbit horseradish peroxidase conjugate by adding 1 µL of goat anti-rabbit horseradish peroxidase conjugate antibody to 4999 µL of Assay/Diluent buffer.
4. Wash Buffer Prepare the Wash Buffer by diluting 15 mL of the supplied concentrate with 135 mL of deionized water. This can be stored at room temperature until the kit expiration date.
Sample Preparation
Adherent Cells
1. Culture cells (one 10-cm plate, ~ 107 cells) to approximately 80-90% confluence. Stimulate cells with activator or inhibitor as desired.
2. Aspirate the culture media and wash twice with ice-cold PBS.
3. Completely remove the final PBS wash and add ice-cold 1X Assay/Lysis Buffer to the cells (0.5 – 1 mL per 10 cm tissue culture plate).
4. Place the culture plates on ice for 10-20 minutes.
5. Detach the cells from the plates by scraping them with a cell scraper.
6. Transfer the lysates to appropriate size tubes and place on ice.
7. If nuclear lysis occurs, the cell lysates may become very viscous and difficult to pipette. If this occurs, lysates can be passed through a 27½-gauge syringe needle 3-4 times to shear the genomic DNA.
8. Clear the lysates by centrifugation for 10 minutes (12,000 x g at 4 °C).
9. Collect the supernatant and store samples (~1-2 mg of total proteins) on ice for immediate use,or snap freeze and store at – 70 °C for future u
Suspension Cells
1. Culture cells and stimulate with activator or inhibitor as desired.
2. Perform a cell count, and then pellet the cells by centrifugation.
3. Aspirate the culture media and wash twice with ice-cold PBS.
4. Completely remove the final PBS wash and add ice-cold 1X Assay/Lysis Buffer to the cell pellet (0.5 – 1 mL per 1 x 107 cells).
5. Lyse the cells by repeated pipetting.
6. Transfer the lysates to appropriate size tubes and place on ice.
7. If nuclear lysis occurs, the cell lysates may become very viscous and difficult to pipette. If this occurs, lysates can be passed through a 27½-gauge syringe needle 3-4 times to shear the genomic DNA.
8. Clear the lysates by centrifugation for 10 minutes (12,000 x g at 4 °C).
9. Collect the supernatant and store samples on ice for immediate use, or snap freeze and store at – 70 °C for future use.
Blood Samples
1. Blood can be assayed directly, but for most assay purposes, it is either allowed to clot or is centrifuged down to pellet out red and white cells.
2. Clotting requires several hours at room temperature, and the clear yellow liquid, the serum, can be used for Apolipoprotein A1analysis. More rapid and convenient is to spin the blood down at top speed in an Eppendorf centrifuge and take the clear yellow liquid, the plasma, for analysis. Workable results have been obtained with blood, serum and plasma, but the kit has been standardized on plasma for reproducibility.
3. A series of blood samples can be taken and frozen at -20°C or lower. Then, when a complete series of samples have been collected they can be thawed out and the red and white cells can be pelleted out in microfuge tubes at top speed for 5 minutes in a microfuge centrifuge. The plasma is then run in the ELISA.
Assay Procedure
1. Place the desired number of strips in the strip well plate holder. Return unused strips to the foil pouch. Tape may assist in holding the wells in place during the assay.
2. Add 100 µL of standards or samples to wells (see reagent preparation section). It is recommended that standards and samples be run in duplicate. Note: A standard curve must be run at each setting.
3. Seal the plate with a plate sealer. Incubate the plate for 1 hour at 37℃ with gentle shaking.
4. IMPORTANT WASH STEP: Gently remove the plate sealer and wash the plate at least 3 times. Thorough washing of the plate is extremely important to reduce background. We recommend using a multi-channel pipette to fill each well with 200 µL of diluted Wash Buffer. Fluid removal from the wells is best accomplished by inverting the plate over a sink and flicking the fluid out of the wells and then blotting the plate on clean paper towels. Repeat this procedure for a total of 3 times.
5. Add 100 µL of the diluted biotin-labelled rabbit anti-Apolipoprotein A1 polyclonal antibody (see reagent preparation section) to each well. Cover the plate and incubate the plate for 1 hour at 37℃ with gentle shaking. 6. Wash as described in Step 4.
7. Add 100 µL of the diluted Streptavidin-conjugated poly-HRP (see reagent preparation section) to each well. Cover the plate and incubate the plate for 1 hour at 37℃ with gentle shaking.
8. Wash as described in Step 4.
9. Add 100 µL of the Substrate solution to every well. Incubate at room temperature for 5~30 minutes without shaking. (Substrates A and B should be mixed together in equal volumes within 15 minutes of use. Protect from light.)
10. Add 100 µL of Stop Solution to every well. This stops the reaction and the plate should be read immediately.
11. Blank the plate reader against the Blank wells, read the optical density at 405 nm, preferably with correction between 570 and 590 nm. If the plate reader is not able to be blanked against the Blank wells, manually subtract the mean optical density of the blank wells from all readings. CAUTION: Bubbles in the wells will cause inaccurate readings. Ensure that all bubbles are removed prior to taking the absorbance reading.
Calculation of Results
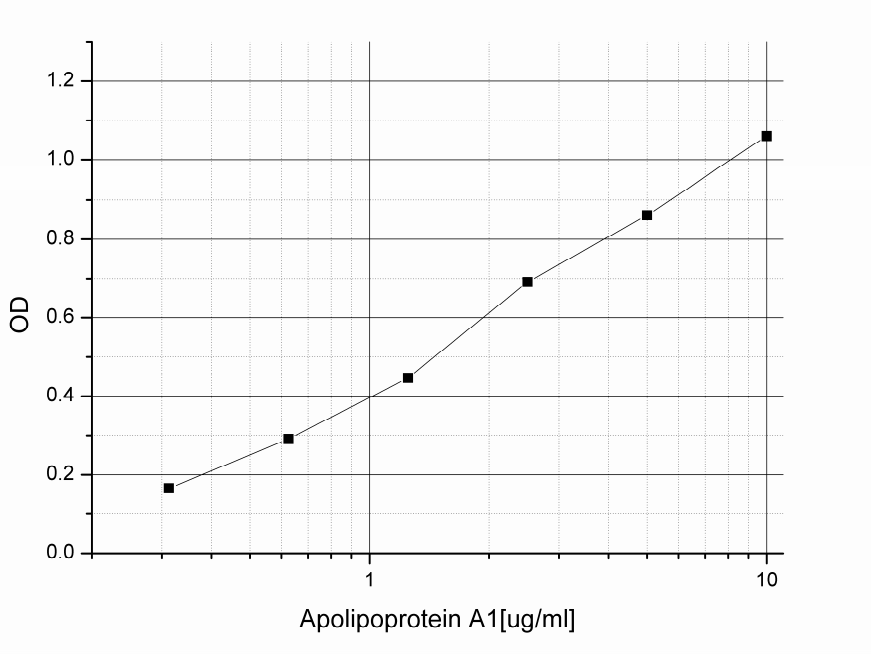
Manual Plotting Plot the standard curve on graph paper. Known concentrations of Apolipoprotein A1 are plotted on the X-axis and the corresponding OD on the Y-axis. The standard curve should result in a graph that shows a direct relationship between Apolipoprotein A1 concentrations and the corresponding ODs. In other words, the greater the concentration of Apolipoprotein A1 in the sample, the higher the OD. The concentration of Apolipoprotein A1 in unknown samples may be determined by plotting the sample OD on the Y-axis, then drawing a horizontal line to intersect with the standard curve. A vertical line dropped from this point intersects the X-axis at the concentration of ApoA1 in the unknown sample. Plate Reader/PC Interface An alternative approach is to enter the data into a computer program with curve fitting software. A good fit can be obtained with a linear regression analysis. Some data points at the top or bottom of the range test may need to be dropped to get a good fit. Currently existing spreadsheet software can perform such plotting.
Typical Standard Curves
These curves must not be used to calculate Apolipoprotein A1 concentrations; each user must run a standard curve for each assay and version used.
 Sensitivity
Sensitivity
Sensitivity: < 0.3 µg/mL