RheB Pull-Down Activation Assay Kit
Cat. # 81201
Introduction
A. Background
Small GTPases are a super-family of cellular signaling regulators. RheB is a member of the Ras-superfamily GTPases. RheB has been shown to interact with C-Raf, Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), TSC2, Ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM), KIAA1303 and Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related. Currently there is no direct assay to measure the activation of RheB GTPases.
The RheB Activation Assay Kit is based on the configuration-specific monoclonal antibody that specifically recognizes RheB-GTP, but not RheB-GDP. Given the high affinity of monoclonal antibodies to their antigens, the activation assay could be performed in a short time. This assay provides the reliable results with consistent reproducibility. These anti-RheB-GTP monoclonal antibodies can also be used to monitor the activation of RheB in cells and in tissues by immunohistochemistry.
B. Assay Principle
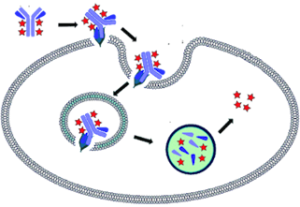
The RheB Activation Assay Kit uses configuration-specific anti-RheB-GTP Mouse monoclonal antibody to measure RheB-GTP levels in cell extracts or in vitro GTPγS loading RheB activation assays. Anti-RheB-GTP mouse monoclonal antibody is first incubated with cell lysates containing RheB-GTP. Next, the GTP-bound RheB is pulled down by protein A/G agarose. Finally, the precipitated RheB-GTP is detected through immunoblot analysis using Anti-RheB Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody.
The anti-RheB-GTP monoclonal antibody can also be used to monitor the activation of RheB in cells and in tissues by immunohistochemistry.
C. Kit Components
1. Anti-RheB-GTP Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Cat. # 26910): 30 µL (1 mg/ml) in PBS, pH 7.4, containing 50% glycerol. This antibody specifically recognizes RheB-GTP from all vertebrates.
2. Protein A/G Agarose (Cat. # 30301): 600 µL of 50% slurry.
3. 5X Assay/Lysis Buffer (Cat. # 30302): 30 mL of 250 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8, 750 mM NaCl, 50 mM MgCl2, 5 mM EDTA, 5% Triton X-100.
4. Anti-RheB Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Cat. # 21098): 50 µL (1 mg/mL) in PBS, pH 7.4, contained 50% glycerol.
5. 100X GTPγS (Cat. # 30303): 50 µl at 10 mM, use 5 µL of GTPγS for GTP-labeling of 0.5 mL of cell lysate.
6. 100X GDP (Cat. # 30304): 50 µl at 100 mM, use 5 µL of GDP for GDP-labeling of 0.5 mL of cell lysate.
7. HRP-Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (Cat. # 29002): 50 µL (0.4 µg/mL) in PBS, pH 7.4, contained 50% glycerol.
D. Materials Needed but Not Supplied
1. Stimulated and non-stimulated cell lysates
2. Protease inhibitors
3. 4 °C tube rocker or shaker
4. 0.5 M EDTA at pH 8.0
5. 1.0 M MgCl2
6. 2X reducing SDS-PAGE sample buffer
7. Electrophoresis and immunoblotting systems
8. Immunoblotting wash buffer such as TBST (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 0.15 M NaCl, 0.05% Tween-20)
9. Immunoblotting blocking buffer (TBST containing 5% Non-fat Dry Milk or 3% BSA)
10. ECL Detection Reagents
E. Example Results
The following figure demonstrates example results seen with the RheB Activation Assay Kit. For reference only.
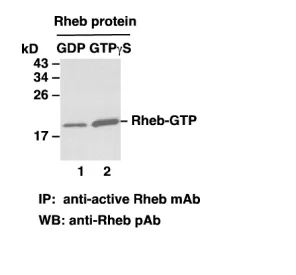
RheB Activation Assay. Purified RheB proteins were immunoprecipitated after treated with GDP (lane 1) or GTPγS (lane 2). Immunoprecipitation was done with the anti-RheB-GTP monoclonal antibody (Cat. # 26910). Immunoblot was with an anti-RheB rabbit polyclonal antibody (Cat. # 21098).
Assay Procedure
A. Reagent Preparation
1X Assay/Lysis Buffer: Mix the 5X Stock (Cat. # 30302) briefly and dilute with deionized water to make 1X buffer. Just prior to usage, add protease inhibitors such as 1 mM PMSF, 10 µg/mL leupeptin, and 10 µg/mL aprotinin.
B. Sample Preparation
Adherent Cells
1. Culture cells (one 10-cm plate, ~107 cells) to approximately 80-90% confluence. Stimulate the cells with activator or inhibitor as desired.
2. Aspirate the culture media and wash twice with ice-cold PBS.
3. Completely remove the final PBS wash and add ice-cold 1X Assay/Lysis Buffer (See Reagent Preparation) to the cells (0.5-1 mL per 10 cm tissue culture plate).
4. Place the culture plates on ice for 10-20 minutes.
5. Detach the cells from the plates by scraping with a cell scraper.
6. Transfer the lysates to appropriate size tubes and place on ice.
7. If nuclear lysis occurs, the cell lysates may become viscous and difficult to pipette. If this occurs, lysates can be passed through a 27½-gauge syringe needle 3-4 times to shear the genomic DNA.
8. Clear the lysates by centrifuging at 12,000 x g and 4°C for 10 minutes.
9. Collect the supernatant and store the sample (~1-2 mg of total protein) on ice for immediate use, or snap freeze and store at -70°C for future use.
Suspension Cells
1. Culture cells and stimulate with activator or inhibitor as desired.
2. Perform a cell count and then pellet the cells through centrifugation.
3. Aspirate the culture media and wash twice with ice-cold PBS.
4. Completely remove the final PBS wash and add ice-cold 1X Assay/Lysis Buffer (See Reagent Preparation) to the cell pellet (0.5-1 mL per 107 cells).
5. Lyse the cells by repeated pipetting.
6. Transfer the lysates to appropriate size tubes and place them on ice.
7. If nuclear lysis occurs, the cell lysates may become viscous and difficult to pipette. If this occurs, lysates can be passed through a 27½-gauge syringe needle 3-4 times to shear the genomic DNA.
8. Clear the lysates by centrifuging at 12,000 x g and 4°C for 10 minutes.
9. Collect the supernatant and store sample on ice for immediate use, or snap freeze and store at -70°C for future use.
C. In vitro GTPγS/GDP Protein for Positive and Negative controls
Note: In vivo stimulation of cells will activate approximately 10% of the available RheB, whereas in vitro GTPγS protein loading will activate nearly 90% of RheB.
1. Aliquot 0.5 mL of cell extract (or 1 µg of purified RheB protein) into two microcentrifuge tubes.
2. To each tube, add 20 µL of 0.5 M EDTA (final concentration of 20 mM).
3. Add 5 µL of 100 X GTPγS (Cat. # 30303) to the first tube as a positive control.
4. Add 5 µL of 100 X GDP (Cat. # 30304) to the second tube as a negative control.
5. Incubate both tubes at 30°C for 30 minutes with agitation.
6. Stop loading by placing the tubes on ice and adding 32.5 µL of 1 M MgCl2 (final concentration of 60 mM).
D. Affinity Precipitation of Activated G Protein
1. Aliquot 0.5-1 mL of cell lysates (about 1 mg of total cellular protein) to a microcentrifuge tube.
2. Adjust the volume to 1 mL with 1X Assay/Lysis Buffer (See Reagent Preparation).
3. Add 1 µL anti-RheB-GTP antibody (Cat. # 26910).
4. Prepare the protein A/G Agarose bead slurry (Cat. # 30301) by resuspending through vertexing or titrating.
5. Quickly add 20 µL of resuspended bead slurry to above tube.
6. Incubate the tube at 4°C for 1 hour with gentle agitation.
7. Pellet the beads through centrifugation at 5,000 x g for 1 min.
8. Aspirate and discard the supernatant (making sure not to disturb or remove the bead pellet).
9. Wash the beads 3 times with 0.5 mL of 1X Assay/Lysis Buffer, centrifuging and aspirating each time.
10. After the third wash, pellet the beads through centrifugation and carefully remove all the supernatant.
11. Resuspend the bead pellet in 20 µL of 2X reducing SDS- PAGE sample buffer.
12. Boil the sample for 5 minutes.
13. Centrifuge it at 5,000 x g for 10 seconds.
E. Western Blot Analysis
1. Load 15 µL/well of pull-down supernatant to a polyacrylamide gel (17%). It is recommended to include a pre-stained MW standard (as an indicator of a successful transfer in step 3 below).
2. Perform SDS-PAGE following the manufacturer’s instructions.
3. Transfer the gel proteins to a PVDF or nitrocellulose membrane following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Note: Steps 4-11 are at room temperature with agitation
4. Following electroblotting, immerse the PVDF membrane in 100% Methanol for 15 seconds, and then allow it to dry at room temperature for 5 minutes.
Note: If Nitrocellulose is used instead of PVDF, step 4 Should be skipped.
5. Block the membrane with 5% non-fat dry milk or 3% BSA in TBST for 1 hr at room temperature with constant agitation.
6. Wash the blotted membrane three times with TBST, 5 minutes each time.
7. Incubate the membrane with Anti-RheB Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Cat. # 21098), which has been freshly diluted 1:50~500 (depending on the amount of RheB proteins in your sample) in 5% non-fat dry milk or 3% BSA in TBST, for 1-2 hr at room temperature with constant agitation or at 4°C overnight.
8. Wash the blotted membrane three times with TBST, 5 minutes each time.
9. Incubate the membrane with a secondary antibody (Cat. # 29002), which is freshly diluted 1:1000 in 5% non-fat dry milk or 3% BSA in TBST, for 1 hr at room temperature with constant agitation.
10. Wash the blotted membrane three times with TBST, 5 minutes each time.
11. Use the detection method of your choice such as ECL.